Table of Contents |
There is quite a large gap between equipment, electricity meters, and their power usage, resulting in a significant loss rate. This lack of proper measurement and electric optimization has been a not-so-easy problem to solve – until the arrival of the DIN Rail Meter.
A DIN Rail meter is a standard-type metal rail used for mounting circuit breakers and industrial control equipment in equipment racks. Additionally, it acts as a mechanical support structure for different types of small electrical parts.
DIN stands for Deutsches Institut fur Normung, meaning German Institute for Standardization. DIN became the official symbol for technical standardization in Germany in the 1970s.
1. DIN Rail Meter - Performance
DIN Rail meters combine industrial energy measurement systems with intuitive installation, compact sizing, and robust two-way communication protocols. These meters achieve outstanding levels of performance while remaining a low-investment alternative, offering the following features:
- Total active power measurement and recount into the energy;
- RS-485 serial port communication protocols;
- Compact size, offering a width which will always be 18mm, or a multiple of this value, ideal for matching with miniature circuit breakers;
- Lead seals offering anti-theft features;
DIN Rail meters outperform traditional meters in all measurable aspects.
2. DIN Rail Meter - Applications
Until recently, the intrinsic relationship between supply and demand in the niche of energy has been hard to control and understand. Several key factors are vital for optimal power measurement. However, only two stand out: accurate energy consumption measurement and user electricity consumption. Both are impossible to achieve using traditional induction meters, which is where DIN Rail meters come into play.
During a fixed period, the DIN Rail meter measures the electricity consumption to deliver base values for the electricity prices. The DIN Rail meter achieves a significant workload reduction while optimizing the energy consumption efficiency and balancing demand and supply by following two simple rules, if the power output is enough, prices can go down, encouraging users to use more power. However, if the power output is not enough, prices will go up, making it less encouraging for users to consume electricity.
3. DIN Rail Meter - Prospects
DIN Rail meters rely heavily on the following three key points:
3.1 Cutting-Edge Performance
- Optimal electric energy measurement;
- Anti-theft properties;
- Real-time monitoring;
- Information interaction;
- Automatic control;
- Applicability to different environments;
- Different installation conditions.
3.2 Low Cost
DIN Rail meters offer a reasonable, safe, and economically viable energy consumption. A DIN Rail meter relies on a robust digital information network powered by a smart-grid, where ordinary residential users can evaluate and handle their household pieces of equipment in real-time through the main panel display or over the Internet.
3.3 Standardization
DIN Rail meters are some cutting-edge electric measurement equipment that will reach and operate nationwide. They will optimize several variables such as costs, after-sales, management, measurement, and workload efficiency.
4. CHINT DIN Rail Meters
Since 1984, CHINT has been a leading global provider of efficient and autonomous energy solutions. Specializing in low-voltage electrics, CHINT Electrics, a CHINT Global subsidiary, ranks as one of the Top 50 Asian companies with an A-share market in the niche. The following two models of DIN Rail meters feature high-level performance, ease of installation, cutting-edge metering solutions, reliability, convenience, innovation, eco-friendliness, and energy efficiency.
4.1 DTSU666 Three Phase DIN Rail Meter
The DTSU666 Three Phase DIN Rail Meter weighs only 400g and measures 98x65x72mm, making it easy to install and handle. With a Class Accuracy of 1.0, this meter can measure frequency, power factor, total kWh and kVarh, and instantaneous kW, kVar, Irms, and Vrms. The LCD has a 7-character segment on a large 48x16mm panel. Lastly, this DIN Rail meter has a low power consumption, at less than 1W, 5VA. Other tech specs include:
- Operating Range Limit: -40C to +75C
- Communication Protocol: RS-485 Serial Port
- IP Rating: IP54 (protected from limited dust ingress and low-pressure water jets sprayed from any direction, including limited water ingress)
- Operating Frequency: 50Hz or 60Hz
The DTSU666 Three Phase DIN Rail Meter is ideal for accurately measuring the energy consumption at camping sites, industrial factories, nautical ports, corporate buildings, large housing blocks, etc.
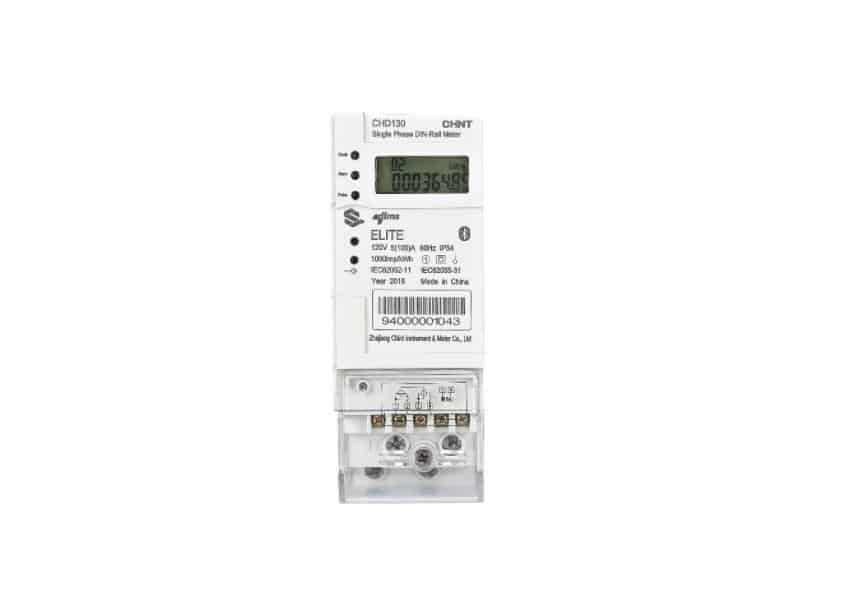
4.2 CHD130 Single Phase DIN Rail Meter
The CHD130 Single Phase DIN Rail Meter is slightly heavier and broader than the Three Phase model, weighing 600g and measuring 140x90x52mm. However, these values do not influence the ease of installation and product handling. Also equipped with a Class Accuracy of 1.0, this meter can measure post-paid and pre-paid energy consumption. Other measurements incorporate total kWh, instantaneous kW, Irms, and Vrms. The LCD panel measures 33x13mm. Finally, this model also has a low power consumption, at less than 1W, 5VA in the voltage circuit. Other tech specs include:
- Operating Range Limit: -40C to +75C
- Communication Protocols: RS-485 Serial Port, M-Bus, PLC, RF, and Bluetooth (optional)
- IP Rating: IP54 (protected from limited dust ingress and low-pressure water jets sprayed from any direction, including limited water ingress)
- Operating Frequency: 50Hz or 60Hz
- Real-time Clock: Accurate within 0.5 seconds per day at 23C
- Built-in Battery: 10-year backup time with power
- Event Logs: Standard, tampering attempt, control, and grid events with a built-in customizable event alarming system (LED and buzzer)
- Ultra Anti-tamper: 20-digit security token protocol, input via keyboard or remote communication
The CHD130 Single Phase DIN Rail Meter is ideal for accurately measuring the energy consumption at residential homes, small offices, and other low-demand establishments.
5. Conclusion
Traditional grids and their gadgets are slowly becoming a thing of the past. Induction meters are no longer a reality, while electronic meters with only one-way communication systems will also become obsolete.
The latest trends in energy-efficient grids and conscious consumption now rely heavily on DIN Rail meters with two-way communication protocols. They outperform traditional induction meters in all aspects, all while also being more eco-friendly, versatile, secure, and more efficient in the short and the long run.
Regardless of project size, for industrial or commercial uses, the DTSU666 Three Phase DIN Rail Meter will most definitely meet all of the criteria. For residential houses and small-sized offices, the CHD130 Single Phase DIN Rail Meter is the go-to option to guarantee money-saving, efficient energy consumption.