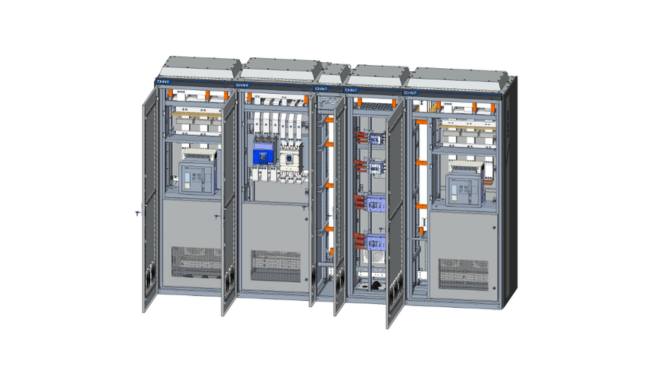
Table of Contents |
In recent years, with global warming and increasingly depleted fossil fuels, the development and utilization of renewable energy has received increasing attention from the international community vigorously developing renewable energy and helping enterprises to transform their energy structure into a zero-carbon era, to achieve carbon peak and carbon neutrality.
Harmony has become the consensus of all countries in the world. Among them, solar energy is one of the main ways to achieve carbon neutrality with its clean, safe, inexhaustible advantages. The demand for photovoltaic equipment has surged, the global installed capacity has continued to rise, and the photovoltaic market has begun to usher in a golden age.
The International Energy Agency (IEC) predicts that renewable energy will become the world’s largest source of electricity around 2030. Nearly 60% of global electricity investment between 2015 and 2040 will flow into the renewable energy sector.
Global PV Installed Capacity
With the improvement of cell conversion efficiency, the market competition of photovoltaic power generation has become prominent. Since the realization of photovoltaic price parity in 2019, the photovoltaic industry has begun to show green shoots.
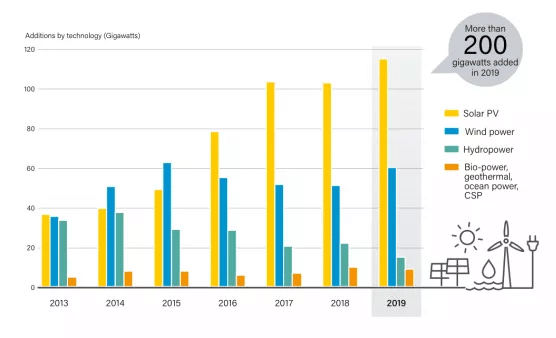
The supply chain from silicon materials to silicon wafers, cells, and modules continues to solidify increasing the installed capacity of renewable power generation by 200 GW, of which 115 GWis photovoltaic. The contribution of photovoltaic power generation is close to 3.0% of the world’s electricity demand whilst in the EU it is close to 5%.
According to the forecast of the Photovoltaic Industry Association, the annual global photovoltaic installed capacity will reach 200 GW in 2025, and the compound growth rate will reach more than 10% in the next five years.
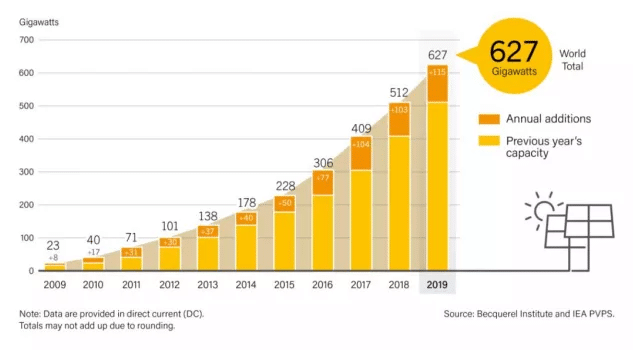
Between 2008-2011 as the financial crisis deepened the development of global photovoltaic installed capacity stalled. However, from 2016 to 2019, driven by government subsidies and policies, the photovoltaic industry grew rapidly. As of the end of 2019, the capacity of the global cumulative photovoltaic installed was 627 GW.
Global PV Market Segmentation
2019 was the year when the photovoltaic industry entered a mature period of marketization. The cost of photovoltaic power generation has fallen after parity and household photovoltaic use has further developed. The photovoltaic industry has ushered in large-scale applications and the volume has grown by orders of magnitude whilst smart grid, multi-energy complementation, and power storage form a more complete system.
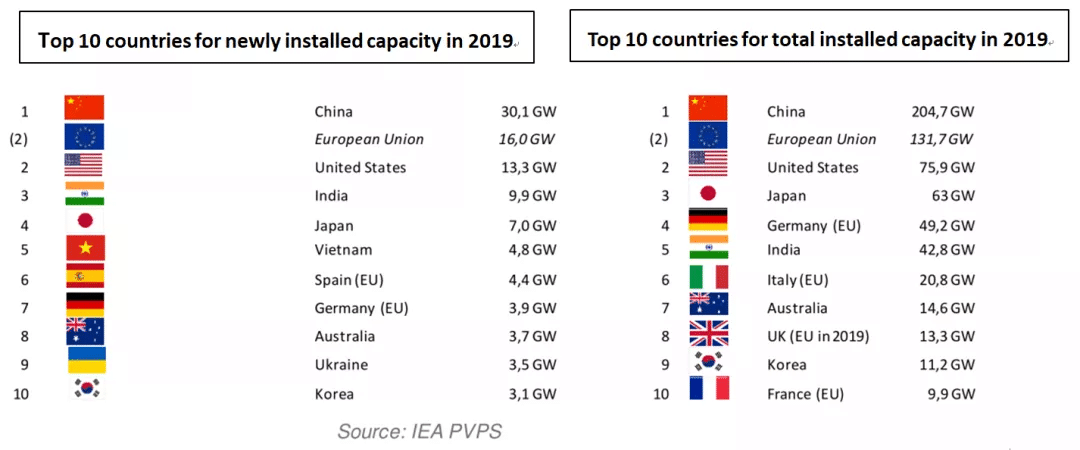
In 2019, the lowest threshold for the top 10 countries with new installed capacity globally exceeded 3 GW, and China’s total installed capacity of photovoltaics ranked first in the world, reached 204 GW. The annual global electricity consumption was 72,255 billion kWh, of which, the photovoltaic power generation reached 224.2 billion kWh, which can meet about 3% of the global demand.
Established photovoltaic countries, such as France, the Netherlands and Turkey, have achieved a relatively high degree of completion in the photovoltaic industry and have therefore fallen out of the top ten new installations. Vietnam and Ukraine entered the top ten list for installed capacities in 2019. Due to the level of installed capacity in the past, the top ten countries with cumulative installed capacity have shown more inertia.
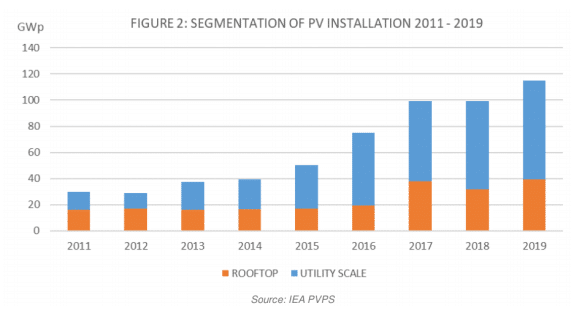
Compared with 2018, the technological advancement of the photovoltaic industry and the vigorous promotion of national bidding plans have resulted in an increase in the absolute number of distributed photovoltaic applications, and the photovoltaic industry has also begun to diversify.
Floating photovoltaic power stations have increased the scale of large-scale power station applications, and building integration of photovoltaics has begun to be widely used in the construction field as a supplementary form of building-integrated solar energy. The absolute number of large ground power stations has also increased. Other emerging markets, such as agricultural photovoltaics show interesting potential but poor market maturity.
The photovoltaic industry is no longer an independent industry, but an indispensable diversified ecological co-builder in the global “dual-carbon” construction arena. As an enterprise deeply cultivating the industrial and energy Internet fields, CHINT is always paying attention to the development of international new energy industry trends. In the next issue, we will introduce the development status of the global photovoltaic industry.