Table of Contents |
A miniature circuit breaker (MCB) offers excellent protection to electrical circuits. It prevents damage from short-circuits and overloads in homes, commercial properties, and many other settings. Used commonly in buildings, MCBs provide circuit protection while functioning as switches for loads. They are compact and compatible with distribution boards. With their widespread usage, electricians and homeowners should learn to correctly read the nameplate information of MCBs to ensure safe installation and operation.
Significance of Correctly Reading the Miniature Circuit Breaker Nameplate
The nameplate of a miniature circuit breaker contains crucial technical specifications that define its intended use and safety ratings. Incorrectly identifying these details can compromise the protection of circuits and electrical loads. Installers need to verify that the MCB selected matches the circuit requirements in terms of voltage, current, and breaking capacity.
Homeowners also need to understand the nameplate to properly maintain the MCB products in their electrical panels. Misreading technical markings could potentially lead to overloading, short-circuiting, and safety hazards over time.
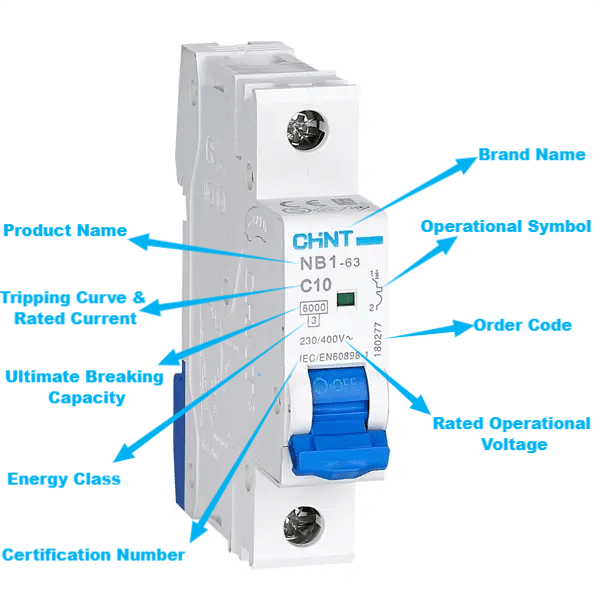
Nameplate Information Breakdown
Let’s break down the key nameplate information using the popular CHINT NB1-63 miniature circuit breaker as an example:
Brand Name
The brand name “CHINT” occupies the top-left corner. This clearly identifies the manufacturer who designed, tested, and warrants the performance of the circuit breaker.
Product Name
Located centrally below the brand name is the product name “NB1-63,” which precisely labels the miniature circuit breaker model. Electricians can reference this when looking up technical documentation or spare parts.
Order Code
On the top-right side, the vertically aligned order code “180277” allows accurate traceability and re-ordering if needed.
Tripping Curve and Rated Current
Represented as “C10”, the tripping curve “C” refers to the current-time characteristics for tripping during overloads or faults. The “10” is the rated current value. It specifies the maximum load current this breaker is rated to protect, i.e., 10A.
Rated Operational Voltage
The operational voltage rating of “230/400V” covers single and three-phase power system voltages to ensure safe interruption under normal or fault conditions.
Ultimate Breaking Capacity
As “6000”, this value confirms the breaker can reliably clear severe short-circuit faults without damage or hot gas emission.
Energy Class
The number “3” denotes the energy absorption capability during tripping to minimize arcing and spatter for user safety.
Certification Number
Listed as “IEC/EN 60898-1”, this certification verifies that the miniature circuit breaker complies with international product standards for construction and performance testing.
Operational Symbol
Located graphically on the right side, the status symbol provides an at-a-glance indication outside of the distribution board for isolation verification.
Products Highlight: NB1 and NXB Miniature Circuit Breakers
Founded in 1984, CHINT is a global leader in smart energy solutions. Over the past 4 decades, the company has focused on industry and brand building through “Green Energy, Intelligent Electric and Smart Low-carbon” segments. The company has manufacturing bases in 16 countries. It provides dependable energy solutions for sustainable development.
Two of its top products in the miniature circuit breaker category include:
NB1 Miniature Circuit Breaker
The NB1 MCB series can protect general lighting and power circuits. The key features of this CHINT MCB include:
- An ultimate breaking capacity of 10kA and energy limitation class 3
- Functions fast closing with extended service life
- Clear ON/OFF visual indication of the circuit status
- Facilitates easy installation and connection
- Equipped with ventilation slots for effective heat dissipation
- Can be assembled with S9、V9、OUVT-1、XF9、XF9J accessories
NXB Miniature Circuit Breaker
- The NXB miniature circuit breaker series is the star of MCBs. Its key characteristics include:
- Robust construction and narrow DIN rail mounting design for industrial and commercial use
- Provides ultra-long mechanical and electrical life for unwavering safety
- Feature a 10mA earth leakage protection capability
- Fast-acting magnetic trip element ensures maximum protection of circuits
Conclusion
Understanding nameplate markings helps ensure that you carefully select and install MCBs for safe and reliable protection. CHINT has nearly four decades of experience in smart energy solutions and a global presence supported by strong R&D. Homeowners and professionals alike can rely on CHINT’s MCBs to efficiently distribute power while preventing hazards from overloads or short circuits. For more information on CHINT’s full portfolio of electrical distribution products, visit the company’s website.